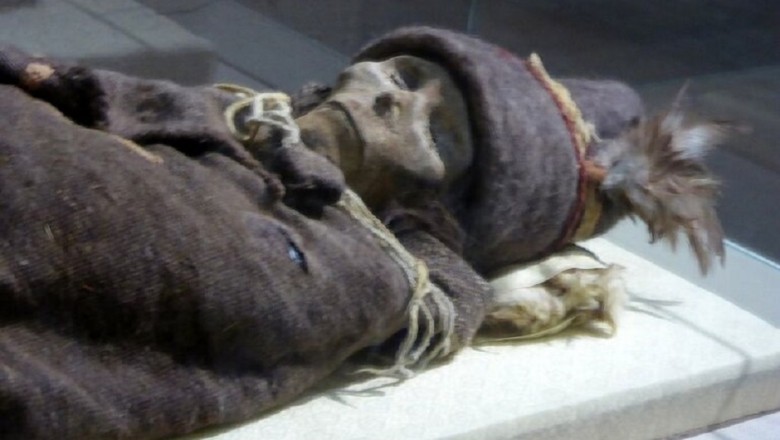

Ancient Tribe Frozen in Time Gets DNA Test That Finally Reveals Their True Identity
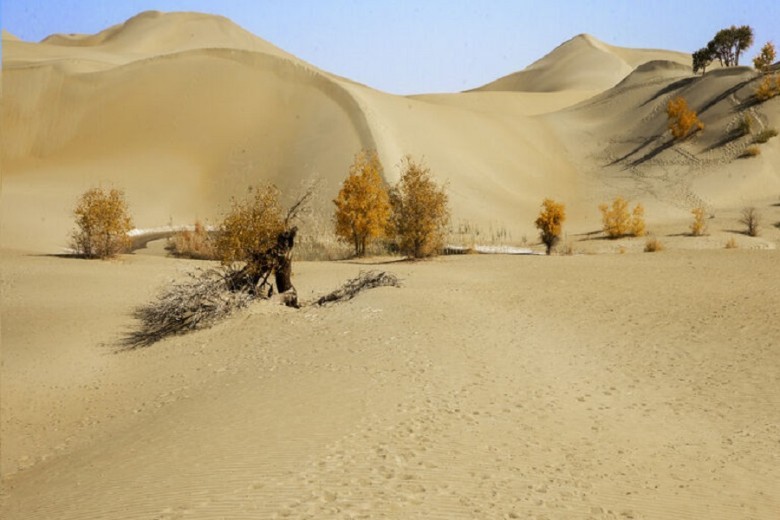
Graves in the Taklamakan Desert
For years, experts have puzzled over the identity of the mummies discovered at the Xiaohe Cemetery in China's Taklamakan Desert due to their unusual appearance and clothing. They seemed to come from outside the region, raising questions about their origins. Did they belong to an unknown civilization or fill a missing link in Chinese history?
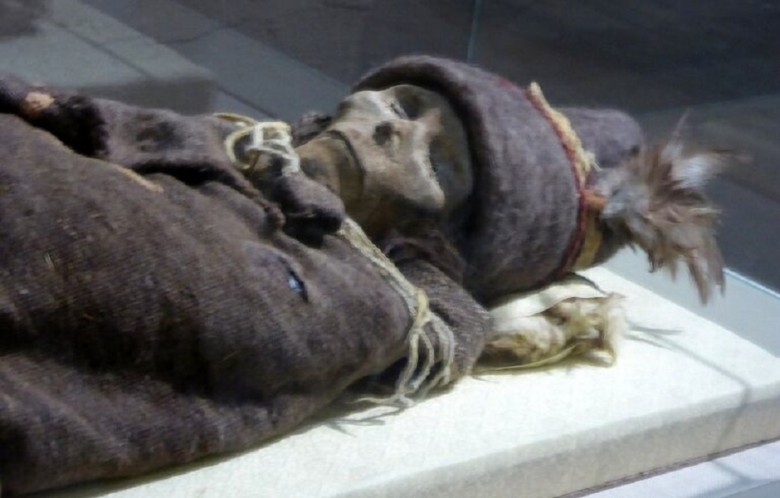

The Xiaohe mummies have sparked countless studies and debates that could potentially rewrite regional history and shed light on ancient civilizations. Researchers are focusing on their cultural and genetic roots. Each discovery raises further questions about their origin and way of life, revealing the complexity of their history.
Western Migrants?
Recently, scientists published genetic study results that resolve the ongoing debate about the origin of these mummies, which had fueled numerous theories and speculations. The question was whether they were the remains of a wandering civilization or indigenous people with a completely different history.

Ideas of mass migrations and lost civilizations fascinate scientists, and every piece of evidence is carefully examined. Solving this puzzle has far-reaching implications for our understanding of ancient migration routes and cultural interactions, with mummy secrets being uncovered through various scientific techniques.
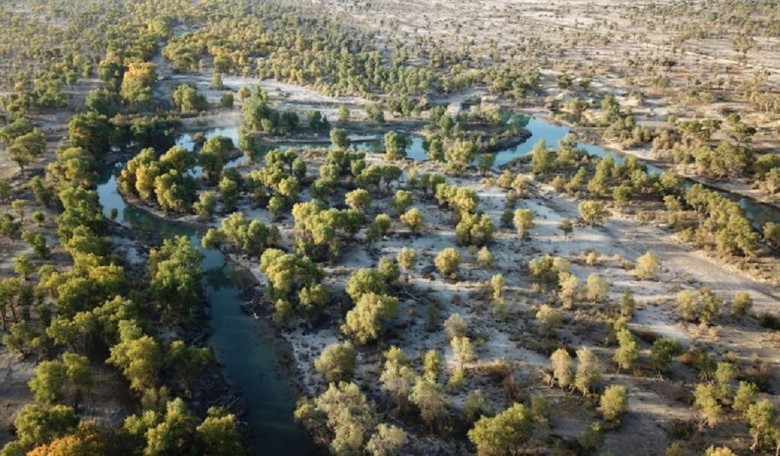
The Tarim Basin
Today, the Tarim Basin is dry, spanning different landscapes and receiving minimal precipitation, making it inhospitable. Thousands of years ago, it is believed to have hosted ancient communities along its rivers, indicating a flourishing civilization based on the artifacts and structures found.
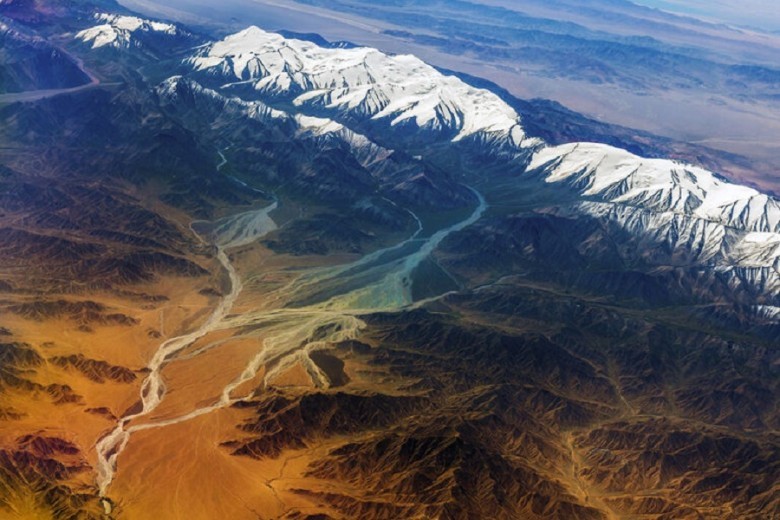

Ancient rivers once flowed through the region, providing support to early communities in the Tarim Basin. Despite the harsh conditions, diverse civilizations adapted and developed strategies to utilize the available resources, with traces of them preserved in the basin's soil.
Ancient Communities
Situated in the heart of the Taklamakan Desert, the Tarim Basin has undergone various climatic and geographical changes over time. Its past is believed to have been rich and vibrant, once nourished by rivers that supplied ancient communities.

Archaeological remains indicate a complex network of interactions between communities, demonstrating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. Climate changes transformed the landscape, leaving behind traces of ancient civilizations in the basin, waiting to be discovered.
The Culture of the Tarim Basin
Over time, changing river courses led to the disappearance of the civilization that thrived in the Tarim Basin. Archaeological studies reveal silent remnants of this once prosperous civilization through excavated structures, tools, and artifacts, providing insights into the life and traditions of these ancient peoples.

Researchers are eager to understand how communities adapted to environmental changes. Advances in archaeology and technology help explore and understand the rich historical fabric of the Tarim Basin, uncovering fragments of lost stories and narratives.
Relics of an Ancient Civilization
Several mummies found in the Tarim Basin in the early 20th century, dating back to 2100 BCE to the 1st century BCE, have raised many questions and theories about their origin and culture. Their excellent preservation condition has allowed for detailed analysis.

Each mummy holds secrets, and refined preservation and study techniques can reveal information about unknown chapters of human history. Discoveries in the Tarim Basin are crucial for understanding the cultural and social dynamics of ancient civilizations in the region.
A Startling Discovery
Despite their old age, the mummies found in the dry environment of the Taklamakan Desert were remarkably well-preserved. These ancient people appeared to be different from the present-day indigenous population, sparking controversies and raising questions about their origins and migration patterns.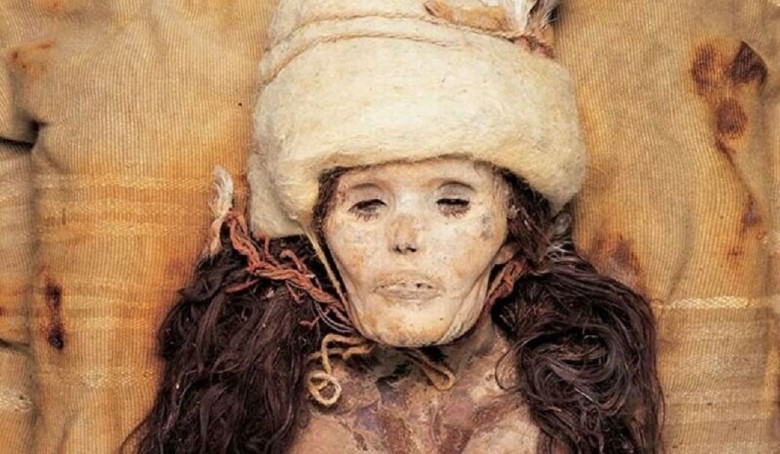
Differences among the mummies led to debates about possible connections with other regions and peoples. The dry environment played a crucial role in their preservation, providing access to information that would have been lost in other contexts.
Caucasian Mummies
The mummies, with their seemingly Caucasian features and non-indigenous clothing, provided valuable insights into manufacturing techniques and patterns of use. This raised questions about cultural exchange and trade in ancient times.

The clothing and accessories of the mummies offer glimpses into their social status and everyday customs, helping to reconstruct aspects of daily life and traditions. The apparent mismatch between the mummies' features and their environment was a recurring theme in academic discussions.
Where Did They Come From?
Over 100 years of theorizing and speculating followed, centering around their unusual appearance and clothing. Advances in science and technology allowed for more detailed examinations and analysis of the remains, exploring various research approaches.

Different disciplines come together to deepen understanding and open up new interpretative possibilities of these enigmatic findings. The dialogues and debates surrounding these discoveries have been fundamental to the advancement of knowledge about ancient civilizations.
Descendants of Indo-Europeans?
The hypothesis that these people were Indo-European ancestors who migrated eastward was extensively examined. These remains indicate agricultural practices occurring long before they became prevalent in the area, possibly pointing to foreign origins.
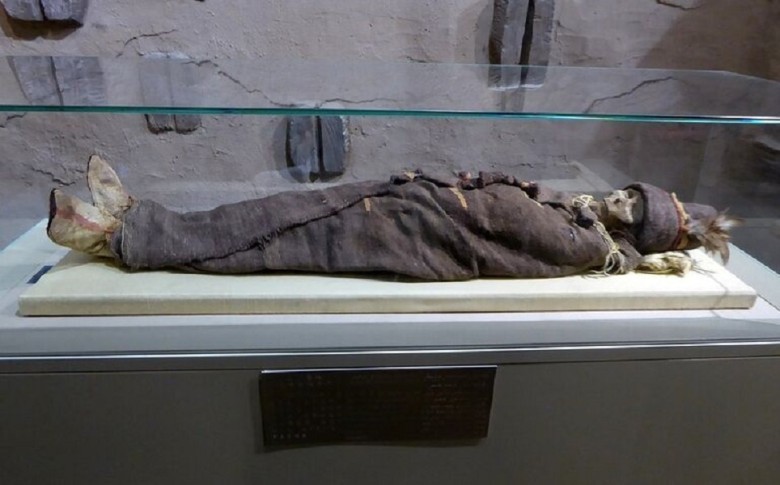

The possibility of cultural interactions and migrations between different regions fascinates archaeologists and historians. Each discovery and analysis contributes to constructing a more complete picture of the cultural and social dynamics of that time.
Xiaohe Cemetery
Experts focusing on mummies from the Xiaohe Cemetery discovered various burial practices and archaeological finds that provided profound insights into the beliefs and values of those ancient communities. The site, discovered in 1910, has witnessed the identification of over 300 graves.
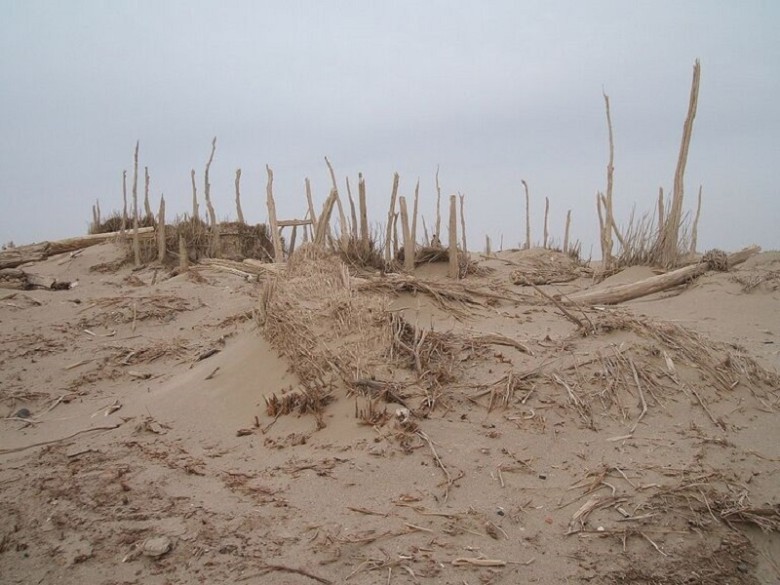

The location and arrangement of the graves reflect the social organization and existing hierarchies in those societies. The methodology employed in the excavations and studies has allowed for the collection of detailed and valuable data.
Folke Bergman
Originally excavated in the 1930s by Folke Bergman, Xiaohe revealed unique burial practices and distinctive grave structures that suggested a complex understanding of the afterlife and the role of the deceased in society. It became evident that this civilization treated their dead with deep reverence and a special cultural significance rarely seen in modern times.
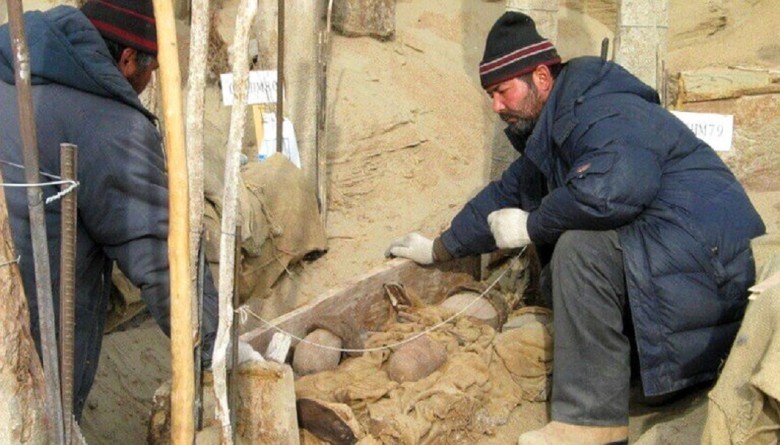

The preservation condition of the bodies allowed for detailed observation of the individuals' features and conditions. Bergman's findings in Xiaohe were a crucial starting point for future research and studies in the region.
Modern Excavations
Decades after Bergman, extensive excavations and studies were conducted, leading to the discovery of over 30 additional mummies. This enriched understanding and allowed for further discoveries through modern research techniques. The ongoing exploration has progressively completed the picture of this ancient civilization.
A detailed analysis of human remains and associated objects revealed previously unknown aspects of these ancient communities. The collaboration of different disciplines was fundamental in addressing the many aspects of the Xiaohe finds. This interdisciplinary approach has expanded our knowledge and provided a deeper understanding of the cultures of that time.
Princess Xiaohe
Among the finds was the "Princess Xiaohe," whose elaborate burial and preserved beauty presented a fascinating puzzle. The details of her burial have provided numerous insights into burial practices and societal values of her time, granting scientists a deep understanding of the culture of the period.
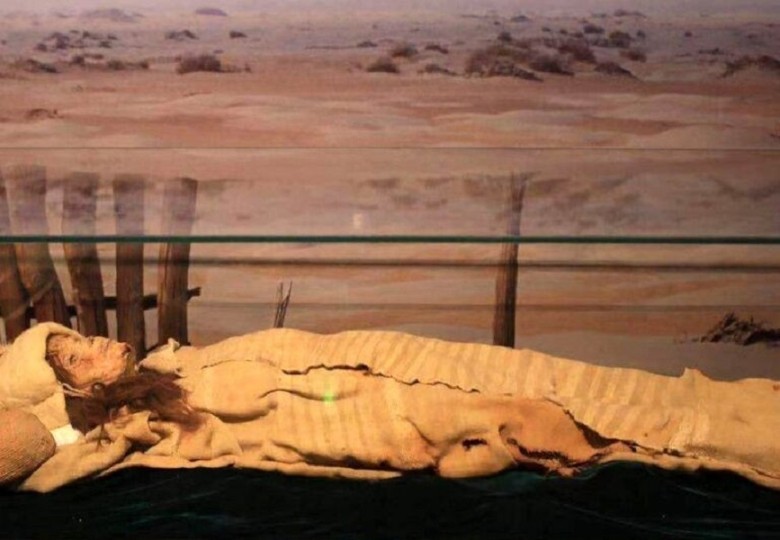

The unique nature of the burial and its excellent preservation allowed for a careful examination of the Xiaohe Princess and her possessions. Her presumed status and striking appearance have sparked numerous theories and hypotheses about her origin and role in the community. Discussions about her identity abound. The artifacts accompanying her were equally fascinating.
Out of Place
The princess posed the same challenges as other mummies, seeming out of place with her non-Asian appearance and unusual textiles. Her enigmatic presence, as well as the presence of similar mummies, constantly challenged researchers, demanding meticulous examination of the available evidence.

Efforts to unravel the secrets surrounding these figures required a multidisciplinary approach. The mystery of Princess Xiaohe and her contemporaries continues to inspire the scientific community to explore and decipher the mysteries of antiquity. Her story remains mysterious, an ongoing subject of scientific interest.
Genetic Study
On October 27, 2021, a study was published in Nature that sought to answer the long-standing question of the origin of the Tarim Basin mummies through extensive genetic research by an international team. The goal was clear: to shed light on the origins of this mysterious population.

This research promised to shed light on the enigmatic inhabitants of this ancient site. The results aimed to uncover the genetic connections and potential migration movements of these ancient civilizations, striving for a deeper connection to the past. The analysis promised groundbreaking discoveries.
Genome Sequencing
DNA extracted from the ancient mummies allowed for a more comprehensive look at the genetic heritage of these people and possibly their places of origin. Thanks to advancements in DNA sequencing technology, the aim was not only to uncover biological details but also cultural and social aspects to trace connections between ancient populations.
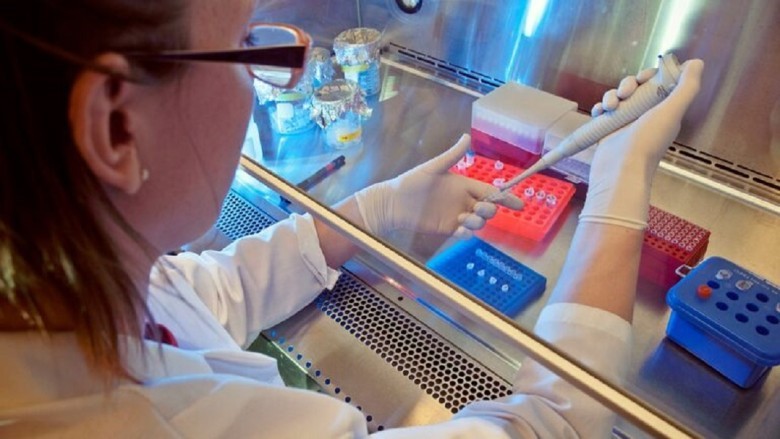

This study represented a monumental advancement in understanding history and ancient cultures by revealing secrets that had remained hidden for millennia. Multidisciplinary work and international collaboration were essential in tackling the diverse challenges and complexities in researching ancient remains. The synergy of experts was crucial, and the value of this collaboration cannot be underestimated.
Solving the Puzzle
Thirteen of these mummies from Xiaohe, believed to date back to around 2000 BCE, were tested to determine if they were non-locals who had migrated eastward to the Tarim Basin. Researchers compared DNA samples with a database of over 300 known genomes to solve the puzzle.

The possibility that these individuals were migrants from other world regions piqued great interest. The analysis of genetic data could reveal migration patterns and the mixing of different communities, intensifying research on this hypothesis. The results could change our understanding of migration.
No Connection to Indo-European Migrants
The study compared genetic data from ancient and modern populations from around the world and concluded that the Xiaohe mummies had no connection to Indo-European migrants, providing a broader view of their ancestry.
A careful comparison of collected data allowed for a more precise understanding of the history of these mummies. The significant diversity in the genetic data was a crucial element in understanding the relationships between different populations. Each finding added to the puzzle. The genetic diversity was fascinating.
Ancient North Eurasians
The study revealed that the 13 individuals exclusively descended from hunter-gatherer societies known as Ancient North Eurasians (ANE) in present-day Russia, who were largely extinct by 8000 BCE. Their genetic material survives in indigenous communities all the way to the Americas.

The discovery of the unique connection with ANE redefined the understanding of the ancestors of the mummies. This provided new perspectives on ancient migrations and cultural exchanges. It also established a living connection to the past through genetic heritage in modern populations. These discoveries are changing history.
Agriculture
The people of Xiaohe had knowledge of advanced processes like agriculture, found in burial sites. This raises significant questions about the acquisition of agricultural knowledge. The presence of agricultural products raises questions about how these societies attained such advanced knowledge.

The evidence of advanced agriculture in a seemingly isolated society was perplexing. This relationship between agricultural practices and global knowledge was crucial. The analysis could shed light on ancient technology and the spread of knowledge. There are many puzzles surrounding these techniques.
Cultural Exchange
Experts believe that these skills emerged due to cultural exchanges rather than migration. Molecular archaeologist Christina Warinner speculates that this research could provide fascinating insights into the development of concepts and ideas. She emphasizes the historical and anthropological significance of the dissemination of skills and knowledge, which could indicate deep cultural exchanges.

Recognizing exchanges enhances understanding of the emergence of cultures and civilizations. Studying the transfer of ideas provides deeper insights into the interactions of different societies. Warinner's reflections offer valuable insights into the dynamics of ancient civilizations. These findings are invaluable for historians.
The Spread of Ideas
Warinner explains that the research illustrates how populations and ideas move and how ideas can spread across different societies, which is central to human development. Understanding the methods and pathways of knowledge transfer is essential for understanding past connections.

The influence of Eurasian civilizations underscores the complexity of ancient intercultural relationships. Warinner's observations frame the understanding of knowledge flow across different times and contexts. These insights are invaluable for historians and researchers.
Genetic Mixing
The study hints at significant interactions without genetic mixing, providing a unique perspective on interpersonal relationships. It questions social dynamics of the time, as cultural exchange does not necessarily lead to the mixing of genetic material.

Preserving genetic integrity amid intense cultural exchange highlights the diversity and selectivity of human interactions. Exploring these aspects sheds light on the many facets of coexistence in the past. The nature of these interactions is crucial for anthropology and history, showing us how societies evolved and changed.
Genetic Isolation
Michael Frachetti suggests that trade does not necessarily mean marrying or having children together. It is possible that the people of the Tarim Basin maintained close cultural ties with surrounding communities while remaining genetically isolated.

Preserving identity and genetic heritage amid significant cultural interactions is enlightening. Understanding this dynamics of exchange provides lessons about diversity and coexistence in antiquity. Frachetti's remarks add a new dimension to the study of past community relationships, helping us better understand ancient civilizations.
Better Adapted
Choongwon Jeong from Seoul National University suggests that agriculture may have been better suited for the Tarim Basin than traditional activities. This raises interest in cultural innovation and adaptation, as well as how agricultural practices adapted to new environments.
The effectiveness of new practices compared to traditional ones is crucial to understanding their adoption. Jeong's research on the adaptability of cultural practices provides insights into the evolution of human societies. Studying agriculture in the Tarim Basin showcases the resilience and creativity of its inhabitants. It is a window into their daily ways of life.
A Compelling Case
Jeong believes that cultural elements such as agriculture were likely more productive in their local environment. He notes that genes and cultural elements do not necessarily migrate together, and the ancient people of the Tarim Basin may have adopted agriculture before their Eurasian cousins.

Assessing the productivity and applicability of different cultural practices is essential. Comparing traditional and new agricultural activities reveals the dynamics in survival strategies. Jeong's conclusions offer valuable understanding of the interaction between genetics and culture in the formation of societies, showing how genetics and culture interact.
Fermented Cheese
The discovery of a type of fermented cheese in Tarim Basin graves dating back 4,000 years opens fascinating possibilities for exploring ancient nutrition and culture. This reveals more about local dietary practices that include dairy products.
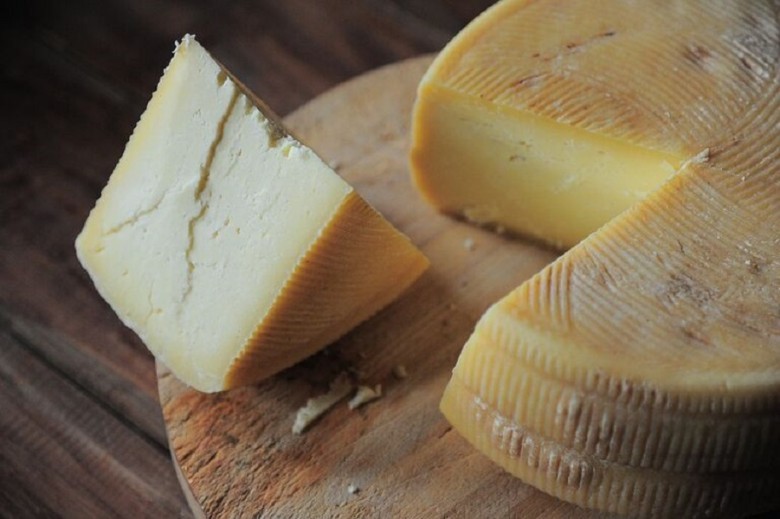

The presence of dairy products in the diet of the Tarim population provides important information about their way of life. Analyzing calcium deposits in teeth offers an innovative method to investigate the dietary history of ancient populations. The role of dairy products in the diet of ancient societies is a highly relevant research topic, providing insights into their eating habits.
Dairying
Results suggest that the early inhabitants of the Tarim Basin consumed dairy products, indicating that pastoralism was already part of their way of life. The significance of these discoveries deepens our understanding of the evolution of human societies and the life and customs of ancient populations.
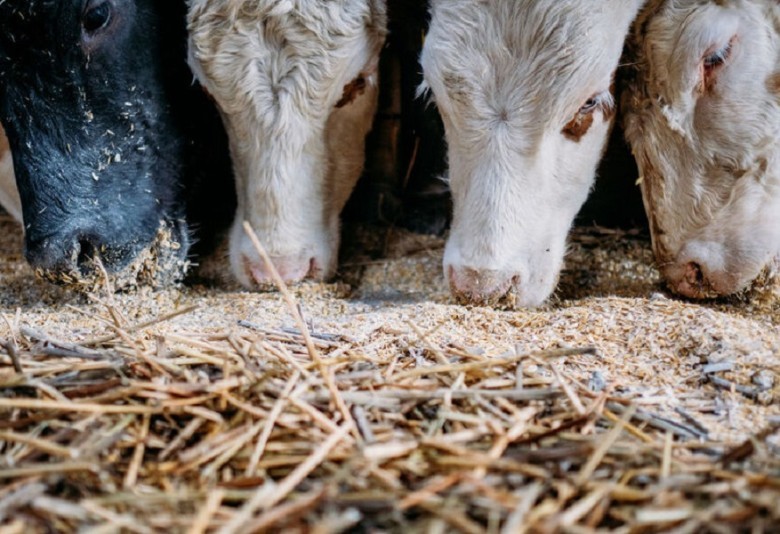

Knowledge of the origin of agricultural and dietary practices is crucial for reconstructing human history. The study details expand the view on adaptation and diversification of dietary practices in antiquity. The integration of dairy pastoralism in the communities of the Tarim Basin is significant for studying their cultural development, showing how they adapted to their environment.
The Bigger Picture
While examining the 13 samples from the Xiaohe cemetery, researchers also analyzed DNA from individuals buried in Dzungaria about 5,000 years ago. This provides insights into genetic connections and differences between ancient populations, unraveling the secrets of forgotten civilizations.

Each sample reveals characteristic aspects of genetic diversity and cultural exchange. This deep genomic analysis illuminates the mysteries of antiquity and lays a solid foundation for future research. It highlights mobility and migration patterns and demonstrates how different human groups related to and interacted with each other. It provides a well-founded basis for further investigation.
The Dzungarians
This detailed analysis of distant genomes from Dzungaria allows scientists to delve deeper into genetic connections and differences between ancient populations. This provides a deeper understanding of the diversity and adaptability of ancient societies.

Each sample uncovers unique aspects of the genetic diversity and admixture of ancient people. The geographical distance between the regions studied offers valuable perspectives on the mobility and migration of human groups in antiquity. Discoveries from this study offer a more comprehensive view of the history and genetic relationships of ancient populations. It connects cultures across continents.
Another Heritage
Despite their geographical proximity, the Dzungarians had a significantly different genetic composition, raising interesting questions about the diversity and adaptability of ancient peoples in different environments and highlighting their contrast in genetic heritage.
The complexity of the genetic heritage of these populations reveals the richness of ancient civilizations. Assessing ancestry and origin is fundamental to deciphering the history and evolution of human cultures. The observed genetic differences provide crucial insights into the lifestyles and relationships of ancient peoples, showing how deeply rooted and diverse our history is.
The Afanasievo
The Dzungarians also descend from the Afanasievo, uncovering unexpected connections and migration patterns. Studying these genetic lineages provides insights into various cultures and their development, showcasing the influence of diverse ancient societies. This genetic connection emphasizes the importance of historical relationships between these ancient peoples, providing a detailed picture of their migratory history.

Analyzing these secondary genetic lineages unravels ancestral secrets about the origins and movements of ancient peoples. Identifying different lines of descent is essential for understanding cultural diversity and adaptation. The relationship between the Dzungarians and the Afanasievo illustrates the complex interplay of heritage and cultural evolution in antiquity. These connections reveal the interconnectedness and influence between ancient cultures.
The Yamnaya
The Afanasievo, considered the oldest people to have lived in southern Siberia, are believed to descend from the Yamnaya, an ancient Indo-European group. Exploring the origins of the Afanasievo sheds light on migration routes and cultural changes of ancient peoples. Each discovery offers a new perspective on the interactions and movements of these early civilizations.

The connection with the Yamnaya highlights the complex network of relationships and descents between different cultures. Studying these ancient civilizations contributes significantly to understanding the evolution of human societies. Exploring the heritage and origins of the Afanasievo is crucial to understanding the prehistory of humanity. Each discovery brings us closer to our roots.
The True Migrants?
The use of Western technologies such as wheeled vehicles and metals by the Afanasievo hints at parts of migration theories, showcasing the diversity of cultural and technological influences in ancient societies. This reveals their adaptability and innovation, and how different cultures have evolved and influenced each other over time.

The interaction with other cultures and the adoption of foreign technologies demonstrate cultural permeability and knowledge exchange. The localization of Afanasievo settlements provides important insights into migration routes and cultural influence zones. Analyzing this technological evidence enables a deeper understanding of the nature and development of ancient cultures. Technology has always been a reflection of society and culture.
The True Migrants?
The use of Western technologies such as wheeled vehicles and metals by the Afanasievo suggests parts of migration theories, revealing the diversity of cultural and technological influences in ancient societies. This demonstrates their adaptability and innovation, and how different cultures have developed and influenced each other over time.
The interaction with other cultures and the adoption of foreign technologies show cultural permeability and knowledge exchange. The localization of Afanasievo settlements provides important insights into migration routes and cultural influence zones. Analyzing this technological evidence allows for a deeper understanding of the nature and development of ancient cultures. Technology has always been a reflection of society and culture.
Much More to Do
It remains unclear whether the Afanasievo were responsible for the cultural exchange that shaped the people of the Tarim Basin. The people of Xiaohe seemed to maintain their ancient way of life while adopting new Western ideas, indicating a convergence of different traditions, practices, and knowledge.

The preservation of old practices while simultaneously embracing new ideas illustrates the dynamics of change and continuity in ancient societies. The dialogue between different cultures has played a crucial role in shaping identities and ways of life. Future research may reveal more details about cultural interaction and knowledge transfer in antiquity. The interplay between tradition and progress is a central theme.
An Oasis of Rivers
According to Warinner, rivers played a crucial role in the ancient communities of the Tarim Basin. The emphasis on river motifs at burial sites highlights the significance of natural resources for the development of ancient communities and how closely their culture and beliefs were intertwined with their environment.

The celebration of water-related motifs reveals cultural and spiritual aspects of the Xiaohe people. Analyzing these motifs provides valuable insights into the beliefs and values of ancient populations. The interaction with the natural environment is crucial to understanding the survival and culture of ancient peoples. Their connection to nature shaped their culture and spirituality.
A Melting Pot of Races
The society of Xiaohe was a melting pot of cultural, though not genetic, influences. The preservation of their identity while adopting new technologies demonstrates the resilience and adaptability of these communities and reflects a convergence of different traditions and knowledge.
The coexistence of diverse cultural influences is a testament to the richness and complexity of Xiaohe society. The exchange and fusion of ideas and cultural practices are central phenomena in the study of human civilizations. This fusion of influences provides deep insight into processes of change, adaptation, and cultural resistance in antiquity. Cultural fusion shaped the identity of the people.
What Comes Next?
Genomic analyses of the Xiaohe mummies are crucial for understanding ancient Asian populations. Continuing such research promises further revelations about human history and could deepen and expand our knowledge of human evolution and our own story.

Studying the Xiaohe mummies unlocks the secrets of ancient human life and development. Expanding our knowledge of ancient populations helps create a more detailed narrative of human history. Immersing ourselves in the genetic mysteries of ancient Asian civilizations is a step forward in deciphering the heritage and evolution of humanity. Each mummy tells its own story.



















Comments
0 comment